代理模式/JAVA动态代理
在学习Spring AOP与RPC的实现时,总会与代理模式密不可分,而日常编码中代理模式也是常用的设计模式之一。学习代理模式与动态代理的实现与作用是非常有益于理解框架的源码实现,并且可以提高抽象思维。本文是个人在学习代理模式以及动态代理的一个小总结,没有过深的探讨。本文不会提及具体动态代理底层字节码框架的实现,之后有机会会补充Javassist和ASM字节码框架的文章。
概念
计算机科学领域的任何问题都可以通过增加一个间接的中间层来解决
代理模式被定位为:为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。在某些情况下,一个对象不适合或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用。
代理设计模式是二十三种着名的GOF设计模式之一 ,它描述了如何解决重复出现的设计问题,以设计灵活且可重用的面向对象软件,即更容易实现,更改的对象,测试和重用。在JAVA中可以实现静态代理、动态代理,而动态代理常用的有JDK Proxy和CGLIB两种方式实现动态代理。
代理模式的核心作用
- 通过代理控制对对象的访问,做为隔离客户端和委托类的中介。
- 借助代理增加一些功能,而不需要修改原有代码。符合开闭原则。
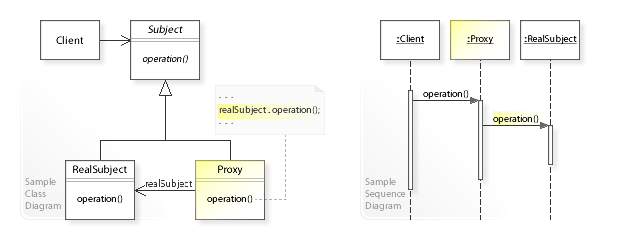
静态代理与动态代理
静态代理一般指的显式指定的代理,由业务实现类、业务代理类两部分组成。业务实现类提供业务的主要实现,业务代理类负责对业务真正的实现进行调用,并且可以进行拦截、过滤、预处理。但静态代理对代码是有很大耦合性的,如果需要大量代理的使用,则需要动态代理。
动态代理则是在程序运行时,根据需求动态的通过反射机制、字节码框架,动态生成代理类进行代理业务操作,极大程度的减少代理模式实现的编码量。
如何实现动态代理
JDK Proxy实现动态代理
java.lang.reflect包中有提供给我们实现动态代理的类库,Proxy和InvocationHandler,来帮助我们实现基于接口的动态代理。
创建代理对象1
2
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException
- ClassLoader loader:被代理类的ClassLoader
- Class<?>[] interfaces:被代理类所实现的接口
- InvocationHandler h:代理对象实例
实现InvocationHandler接口,实现invoke方法,通过反射调用原方法。1
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable;
- Object proxy:调用该方法的代理类的实例
- Method method:代理方法
- Object[] args:代理方法参数列表
下面是一段非常简单的示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public interface IBusiness {
void doSomething();
}
public class BusinessImpl implements IBusiness {
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("do something ...");
}
}
1 | import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; |
由示例可知,借助于JDK proxy实现动态代理的弊端,被代理类必须有接口,JDK动态代理其实也是基本接口实现的。因为通过接口指向实现类实例的多态方式,可以有效地将具体实现与调用解耦,便于后期的修改和维护。
JDK动态代理是利用反射机制在运行时创建代理类的。核心是InvocationHandler。每一个代理的实例都会有一个关联的调用处理程序(InvocationHandler)。对待代理实例进行调用时,将对方法的调用进行编码并指派到它的调用处理器(InvocationHandler)的invoke方法。所以对代理对象实例方法的调用都是通过InvocationHandler中的invoke方法来完成的,而invoke方法会根据传入的代理对象、方法名称以及参数决定调用代理的哪个方法。
关于JDK Proxy动态代理具体实现细节,可以参考深入理解JDK动态代理机制,该篇文章很简洁的介绍了源码。
CGLIB实现动态代理
cglib能够实现基于类的动态代理,生成业务类的子类,覆盖业务方法实现代理,因为采用的是继承,所以不能对final修饰的类进行代理。
Enhancer
实例Enhancer,通过该类对象创建代理实例。
1 | public Enhancer() { |
- setSuperclass:设置代理的父类
- setCallback:设置代理回调
net.sf.cglib.proxy.Callback是一个用于标记的接口,net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer使用的所有回调都会继承这个接口。 - create:默认使用无参构造方法创建目标对象,如果需要调用有参构造方法应该使用net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer.create(Class[], Object[])。该方法的第一个参数指明参数类型,第二个参数指明参数值。参数中的原子类型需要使用包装类。
CallBack
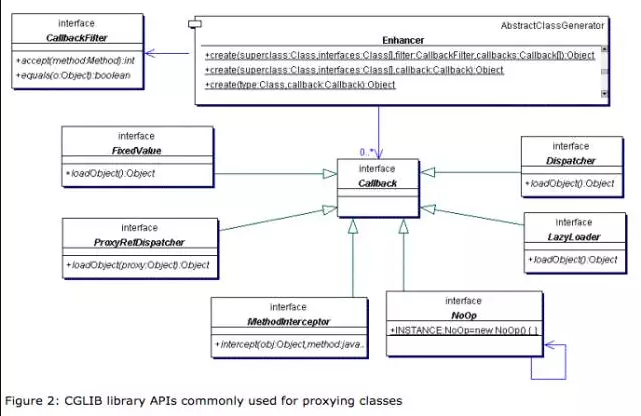
net.sf.cglib.proxy.FixedValue:在强制一个特定方法返回固定值,在特定场景下非常有用且性能高。
net.sf.cglib.proxy.NoOp:它直接透传到父类的方法实现。
net.sf.cglib.proxy.LazyLoader:在被代理对象需要懒加载场景下非常有用,如果被代理对象加载完成,那么在以后的代理调用时会重复使用。
net.sf.cglib.proxy.Dispatcher:与net.sf.cglib.proxy.LazyLoader差不多,但每次调用代理方法时都会调用loadObject方法来加载被代理对象。
net.sf.cglib.proxy.ProxyRefDispatcher:与Dispatcher相同,但它的loadObject方法支持传入代理对象。
net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor:是最常用的回调类型,在基于代理的AOP实现中它经常被用来拦截方法调用。
使用Enhancer创建代理对象
先编写一个简单的代理示例:
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
运行结果
1 | do something ... |
通过运行结果,最后生成的代理类的父类是我们的业务类,由此可以得出结论Enhancer生成的代理对象是设置的Superclass设置的子类。
而我们使用的内置回调NoOp,实际上代理类没有做其他的代理操作,相当于直接调用了父业务类的方法。
使用MethodInterceptor
通过实现MethodInterceptor接口,可以将代理的所有方法调用都会被分派给net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor的intercept方法。intercept方法中可以调用底层对象。
1 | public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable |
- obj:代理对象
- method:被代理的方法
- args:被代理方法的参数列表
- methodProxy:代理方法
1 | import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer; |
运行结果1
2
3
4
5
6method:public void proxy.BusinessImpl.doSomething()
methodProxy:net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy@45ff54e6
after...
do something ...
before...
class proxy.BusinessImpl
关于使用Method还是MethodProxy调用类方法,Method则是被代理类的方法,即通过反射调用。而MethodProxy则是cglib提供的被代理方法的代理。看了一些文章有讲到MethodProxy的执行效率更高,但具体没有研究过,有待验证。
CallbackFilter
Enhancer还提供了CallbackFilter和多个Callbacks,通过下标的方式提供对于具体细化到方法粒度的回调。
1 | public void setCallbacks(Callback[] callbacks) |
因为设置CallbackFilter需要传入CallbackFilter接口实现类
1 | /** |
关于CallbackFilter,我们可以看下accept方法,主要作用为通过方法映射到不同的callback,方法的返回值是enhancer中设置的Callbacks的下标。
举个栗子
先增加两个方法,因为本身与接口无关,所以就直接在类中增加方法了。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public class BusinessImpl implements IBusiness {
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("do something ...");
}
public void doSomethingA() {
System.out.println("do something A ...");
}
public void doSomethingB() {
System.out.println("do something B ...");
}
}
然后实现CallbackFilter,我们先设置方法A和方法B使用第二个Callback,默认使用第一个。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9class DemoCallbackFilter implements net.sf.cglib.proxy.CallbackFilter {
public int accept(Method method) {
if(method.getName().equals("doSomethingA") || method.getName().equals("doSomethingB")){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
这里我们设置CallbackFilter,并且设置Callbacks,第一个设置为默认代理,第二个使用之前例子中的MethodInterceptor。
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
运行结果如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11do something ...
methodName:public void proxy.BusinessImpl.doSomethingA()
methodProxy:net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy@45283ce2
after...
do something A ...
before...
methodName:public void proxy.BusinessImpl.doSomethingB()
methodProxy:net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy@3d71d552
after...
do something B ...
before...
可以看出,通过CallbackFilter实现了对方法粒度的回调过滤。
总结
一般情况下都可以使用JDK动态代理方法来创建代理,对于没有接口的情况或者性能因素,CGLIB是一个很好的选择。而CGLIB是一个强大的高性能的代码生成库。作为JDK动态代理的互补,它对于那些没有实现接口的类提供了代理方案。在底层,它使用ASM字节码操纵框架。本质上来说,CGLIB通过产生子类覆盖非final方法来进行代理。它比使用Java反射的JDK动态代理方法更快。CGLIB不能代理一个final类或者final方法。
参考资料
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_pattern
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/471c80a7e831
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/9a61af393e41?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0
- https://www.cnblogs.com/ygj0930/p/6542259.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/LCcnblogs/p/6823982.html
- https://www.2cto.com/kf/201801/710319.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/6661692.html
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/sS4QYvERlYFZh1EyXuDV3Q

